Swing trading involves capturing short-term price movements in stocks, typically holding positions for days to weeks. It’s a strategy between day trading and long-term investing, aiming for consistent gains. Swing Trading For Dummies serves as a comprehensive guide, helping beginners understand the basics, risks, and strategies to succeed in this lucrative trading style.
1.1 What is Swing Trading?
Swing trading is a strategic approach to trading stocks, focusing on capturing short-term price movements over days or weeks. Unlike day trading or long-term investing, it balances time commitment and market opportunities; As outlined in Swing Trading For Dummies, this method involves identifying trends, managing risks, and executing trades to capitalize on market fluctuations effectively.
1.2 How Swing Trading Differs from Day Trading and Long-Term Investing
Swing trading stands apart from day trading by holding positions overnight, while differing from long-term investing through its focus on short-term gains. Day traders close positions daily, avoiding overnight risks, whereas swing traders ride price waves for days or weeks. Long-term investors aim for gradual growth over years, contrasting with swing trading’s active, tactical approach to market opportunities.
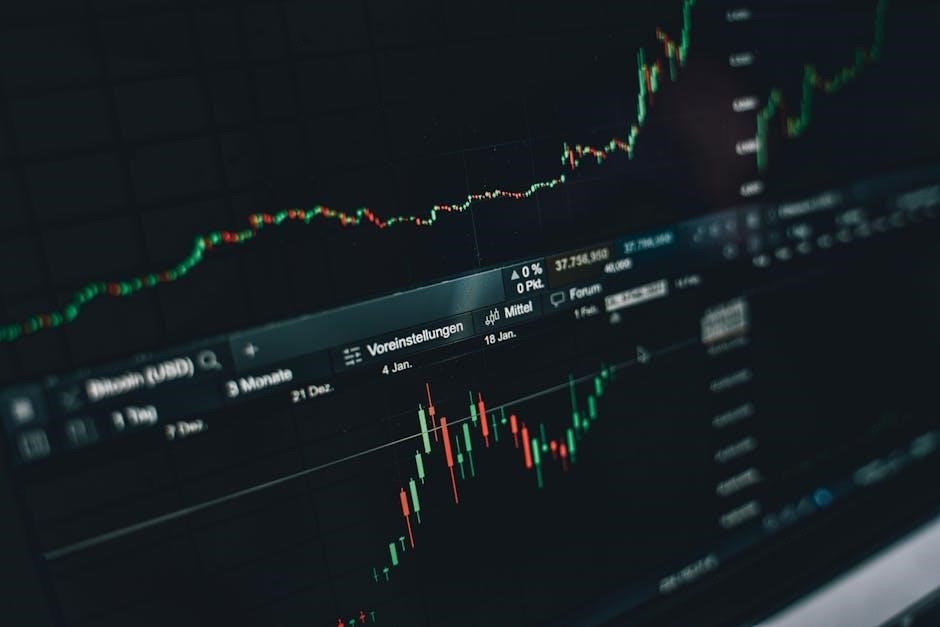

Benefits and Risks of Swing Trading
Swing trading offers a balance between profit potential and manageable risk, appealing to those seeking returns without day trading’s intensity, though market unpredictability poses challenges.
2.1 Why Swing Trading is Popular
Swing trading is popular due to its balance between time commitment and profit potential. It appeals to traders who seek short-term gains without the intensity of day trading. The strategy’s flexibility allows traders to adapt to market trends, making it accessible for both experienced investors and newcomers. Resources like Swing Trading For Dummies have also made it easier for anyone to learn and apply these strategies effectively.
2.2 Potential Risks and Challenges
Swing trading carries risks like market volatility and emotional decision-making, which can lead to significant losses. Overnight gaps in price can also impact trades. While resources like Swing Trading For Dummies offer strategies to manage these risks, they require discipline and continuous learning to navigate effectively.

Essential Swing Trading Strategies
Swing trading strategies like momentum trading, trend following, and breakout techniques help traders profit from short-term market movements. These approaches are detailed in resources like Swing Trading For Dummies, providing clear guidance for execution.
3.1 Momentum Trading
Momentum trading focuses on stocks showing strong price movements. It involves entering trades when upward momentum is confirmed and exiting when it begins to reverse. This strategy requires precise timing and is often used in swing trading to capitalize on short-term trends. Swing Trading For Dummies highlights how to identify momentum stocks using indicators like RSI and MACD, ensuring traders can ride the wave effectively while managing risks associated with rapid price changes.
3.2 Trend Following
Trend following is a core swing trading strategy that involves identifying and profiting from established market trends. Traders use technical indicators like moving averages and trend lines to spot direction and strength. Swing Trading For Dummies emphasizes the importance of staying aligned with the trend, avoiding countertrend trades, and using risk management techniques to maximize gains while minimizing losses in trending markets.
3.3 Breakout and Pullback Strategies
Breakout and pullback strategies are popular in swing trading, focusing on entering trades during price pattern confirmations. A breakout occurs when the price surpasses a resistance level, signaling upward momentum. Conversely, a pullback is a brief reversal within an uptrend, offering a lower entry point. Swing Trading For Dummies highlights the effectiveness of combining these strategies with risk management tools like stop-loss orders to capitalize on trend continuation while minimizing exposure to false breakouts.

Risk Management in Swing Trading
Risk management is essential for swing traders, involving strategies like stop-loss orders to limit potential losses. Position sizing and diversification help manage exposure, while psychological discipline ensures adherence to trading plans. Swing Trading For Dummies emphasizes these tools to protect capital and maintain consistent profitability in volatile markets.
4.1 Setting Stop-Loss Orders
Setting stop-loss orders is crucial in swing trading to limit potential losses. These orders automatically sell a stock when it falls below a predetermined price, protecting capital. Swing Trading For Dummies highlights the importance of placing stop-losses based on volatility and support levels, ensuring traders minimize risk and maintain disciplined exits in volatile markets.
4.2 Position Sizing for Beginners
Position sizing is essential for managing risk in swing trading. Swing Trading For Dummies advises beginners to allocate a small portion of their capital to each trade, ensuring no single loss is catastrophic. By calculating position size based on risk tolerance and account balance, traders can maintain consistent returns and avoid overexposure to market volatility, fostering long-term success.
4.3 The Psychology of Risk Management
The psychology of risk management is crucial for swing traders, as emotions like fear and greed can derail even the best strategies. Swing Trading For Dummies emphasizes the importance of discipline and maintaining a clear mindset. Traders must accept losses as part of the process and avoid over-leveraging. By staying focused and adhering to predefined plans, beginners can build resilience and make rational decisions, ensuring long-term success.

Technical Analysis for Swing Traders
Technical analysis is key for swing traders, involving tools like moving averages, RSI, and chart patterns to identify trends and potential price movements. Swing Trading For Dummies provides a detailed guide on using these indicators effectively to make informed trading decisions and maximize profits.
5.1 Key Indicators for Swing Trading
Swing traders rely on technical indicators like RSI, moving averages, and MACD to identify trends and potential reversals. Relative Strength Index (RSI) helps spot overbought or oversold conditions, while Bollinger Bands indicate volatility and price extremes. Moving Averages smooth price data, revealing trends. These tools, covered in Swing Trading For Dummies, are essential for predicting price movements and timing entries/exits effectively.
5.2 Chart Patterns Every Trader Should Know
Key chart patterns for swing traders include Head & Shoulders, Triangles, Wedges, and Gap Patterns. These formations help predict price reversals or continuations. Support and Resistance levels are also crucial, often highlighted by Double Tops/Bottoms or Bullish/Bearish Engulfing Candles. Swing Trading For Dummies explains how to identify and interpret these patterns effectively, helping traders make informed decisions and maximize profits.

How to Choose the Right Stocks for Swing Trading
Selecting the right stocks involves targeting volatile yet liquid assets. Focus on stocks with high volume and clear price patterns, using both technical and fundamental analysis to identify opportunities. Ensure the stock has sufficient price movement to capitalize on swings, avoiding illiquid or overly stable securities for better trading results, as outlined in Swing Trading For Dummies.
6.1 Identifying Volatile but Liquid Stocks
Identifying volatile yet liquid stocks is crucial for swing trading. Look for stocks with high Average Daily Volume and significant price swings. Use metrics like Beta to gauge volatility. Ensure liquidity by focusing on stocks with tight bid-ask spreads. Avoid illiquid stocks to prevent execution challenges. Tools like Bollinger Bands and RSI can help spot oversold or overbought conditions, aiding in identifying potential swing opportunities, as detailed in Swing Trading For Dummies.
6.2 Using Fundamental Analysis for Stock Selection
Fundamental analysis is vital for selecting stocks in swing trading. Assess a company’s financial health by reviewing income statements and balance sheets. Look for strong revenue growth, low debt, and high margins. Industry trends and competitive advantages are also key. Tools like P/E ratios and P/B ratios help identify undervalued stocks. Combine this with technical analysis for a holistic approach, as recommended in Swing Trading For Dummies to maximize trading success.

Real-World Examples and Case Studies
Real-world examples, like trading tech stocks during earnings season, demonstrate how swing trading works. Successful cases show profits of 15-20% within weeks, teaching valuable lessons.
7.1 Successful Swing Trading Examples
Swing Trading For Dummies highlights real-world examples, such as trading tech stocks during earnings season. These cases show how traders achieve 15-20% profits within weeks by riding momentum. The book also shares strategies like trend following and breakout trading, demonstrating how to identify and capitalize on short-term opportunities effectively. These examples provide practical insights, helping traders refine their skills and build confidence.
7.2 Learning from Common Mistakes
Swing Trading For Dummies emphasizes learning from errors. Common mistakes include overtrading, ignoring risk management, and chasing trends too late. The book highlights the importance of discipline and sticking to a strategy. By understanding these pitfalls, traders can refine their approach, avoiding costly errors and improving their overall performance in the markets.
Educational Resources for Swing Traders
Swing Trading For Dummies by Omar Bassal is a top resource, offering clear guidance for beginners. Online courses and tutorials also provide hands-on learning opportunities.
8.1 Recommended Books: “Swing Trading For Dummies”
Swing Trading For Dummies by Omar Bassal is a must-read for beginners. This comprehensive guide covers swing trading strategies, risk management, and technical analysis. It breaks down complex concepts into simple, actionable advice. The book includes real-world examples, step-by-step trade setups, and essential charts. Perfect for new traders, it helps build a strong foundation and improve trading skills effectively.
8.2 Online Courses and Tutorials
Online courses and tutorials are excellent for mastering swing trading. Platforms like Udemy and Coursera offer courses that cover technical analysis, risk management, and strategy development. These resources provide hands-on learning, often with real-world examples and step-by-step guides. They are ideal for beginners, offering flexible learning to build confidence and skills in swing trading effectively.

Final Tips for Beginners
Start small, focus on risk management, and stay disciplined. Avoid overtrading and analyze each trade’s performance to refine your strategy continuously for long-term success.
9.1 Starting Small and Building Confidence
Beginners should start with small trades to minimize risk and build confidence. Focus on understanding the process, managing emotions, and refining strategies. Avoid overtrading and prioritize learning from each experience. By starting small, you can gradually develop the skills and discipline needed for long-term success in swing trading.
9.2 The Importance of Discipline in Trading
Discipline is crucial for success in swing trading. It ensures adherence to strategies, risk management, and emotional control. Sticking to predefined rules prevents impulsive decisions, while patience helps in avoiding suboptimal trades. Consistent discipline builds resilience, allowing traders to navigate market volatility and maintain long-term profitability, as emphasized in Swing Trading For Dummies.
Swing trading offers a balanced approach for traders, combining short-term gains with manageable risks. By mastering strategies and maintaining discipline, traders can achieve consistent profitability, as outlined in Swing Trading For Dummies.
10.1 Recap of Key Concepts
Swing trading focuses on capturing short-term price movements, leveraging strategies like momentum trading, trend following, and breakout techniques. Essential tools include technical indicators and chart patterns. Risk management, through stop-loss orders and position sizing, is crucial. Combining technical and fundamental analysis helps in selecting stocks. Discipline and patience are vital to avoid common mistakes and achieve consistent profitability in this dynamic trading style.

10.2 Encouragement to Keep Learning
Continuous learning is key to mastering swing trading. Stay updated with market trends, refine your strategies, and explore new tools. Resources like Swing Trading For Dummies and online courses offer invaluable insights. Embrace challenges, learn from mistakes, and remain disciplined. With persistence and dedication, you’ll enhance your trading skills and achieve long-term success in this dynamic field.